Allrun
#!/bin/sh
cd ${0%/*} || exit 1 # Run from this directory
# Source tutorial run functions
. $WM_PROJECT_DIR/bin/tools/RunFunctions
# Get application name
application=$(getApplication)
runApplication blockMesh
runApplication setFields
runApplication $applicationAllclean
#!/bin/sh
cd ${0%/*} || exit 1 # Run from this directory
# Source tutorial clean functions
. $WM_PROJECT_DIR/bin/tools/CleanFunctions
cleanCaseRemove time folders in different processors
rm -r processor*/0.05
Collated files output ,pdf
decomposePar -fileHandler collated
mpiexec -n 8 Solver -parallel -fileHandler collated
multiphase flow simulation
Tutorial LPT
Only for incompressible solver, other solver doesn’t work
kinematicCloudProperties template
Tutorial
Add turbulence model in OpenFOAM 3.0
In interFOAM, there are
1. alphaSuSp
2. correctPhi
3. createFields
4. initCorrectPhi
5. interFoam
6. pEqn
7. rhofs
8. UEqn
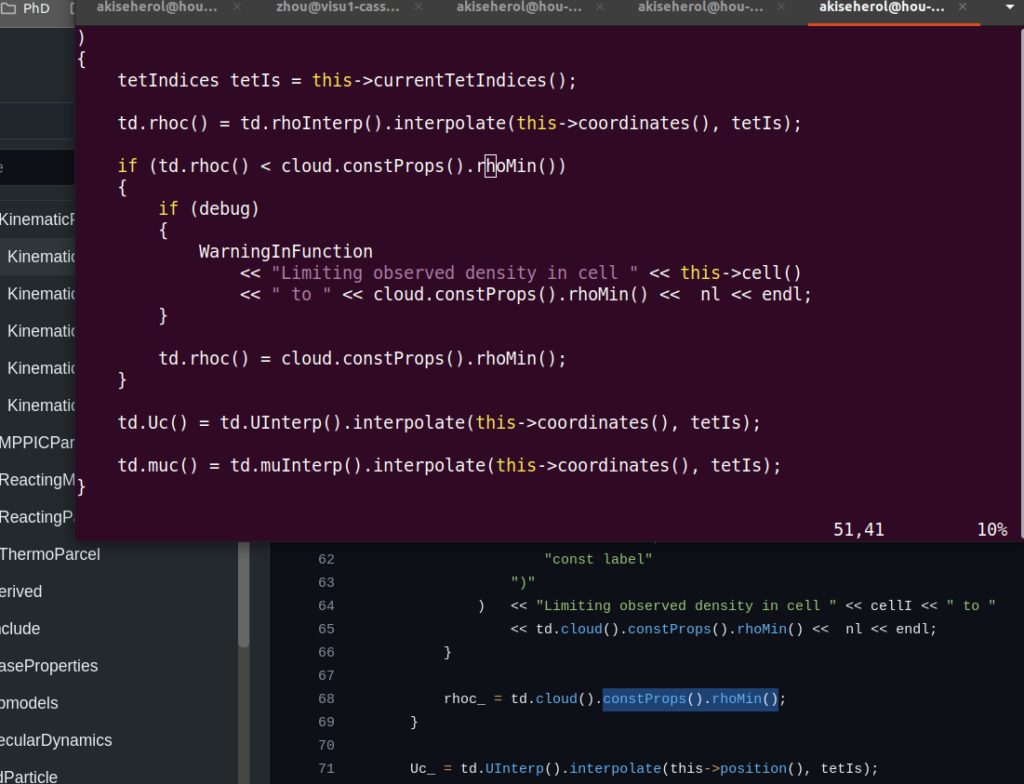
<strong>From</strong>
rhoc_ = td.cloud().constProps().rhoMin();
Uc_ = td.cloud().dispersion().update
(
dt,
cellI,
U_,
Uc_,
UTurb_,
tTurb_
);
<strong>To
</strong>td.rhoc() = cloud.constProps().rhoMin();
td.Uc() = cloud.dispersion().update
(
dt,
this->cell(),
U_,
td.Uc(),
UTurb_,
tTurb_
);
| Adding Thermo to basicKinematicCollidingCloud Adding particles/parcels to kinematicCloud icoUncoupledKinematicCloud postprocess Iteration over particles Running PIMPLE in steady-state mode Linking a velocity field to particles using icouncoupledKinematicParcelFoam https://www.tfd.chalmers.se/~hani/kurser/OS_CFD_2022/ Access particle data in main function Lagrange particles not moving Postprocessing using ParaView https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PL6fjYEpJFi7W6ayU8zKi7G0-EZmkjtbPo https://drive.google.com/drive/folders/1emHuLLkXBkJoCii_4obBy9PNRlK7n1Vq |
Makefile can be run directly as ‘make’
for example
sayhello:
echo “helloworld”
rm: This stands for “remove” and is the command used to delete files or directories.- -rf: These are options that modify the behavior of the rm command:
-r: This option stands for “recursive” and is used to remove directories and their contents recursively. If a directory contains other subdirectories or files, thermcommand will delete them as well.-f: This option stands for “force” and is used to remove files or directories without prompting for confirmation, even if the user does not have write permissions. It suppresses most error messages, making the deletion process more forceful.
A possible bug: Unusual slow-down using collated I/O format
I recently faced the same problem. I am using an explicit solver based on rhoCentralFoam and I’ve to use small time-steps due to high Mach flow. Apparently, as you mentioned the runtime ++ operation takes more and more time with more iterations and using the collated format. I tracked down the issue and it was from
Time.C, setTime() function. The issue is when using collated format it accumulates the time step names in a pointer list and sorts them every time during ++ operation. You can check masterUncollatedFileOperation.C and the setTime() function.
Yet I could not figure out why such is list is required for the collated format but certainly, the size of the pointer list increases with the number of iterations.
hope it helps.